In a Science Magazine article titled, “Firearms and accidental deaths: Evidence from the aftermath of the Sandy Hook school shooting,” economists Phillip B. Levine and Robin McKnight claim to find a causal link between the spike in gun sales after the Sandy Hook shooting and the number of fatal firearms accidents in the “Post-Sandy Hook Window” running from December 2012 to April 2013.
The real issue with this research is found, as usual, in the methods. Levine and McKnight use an eight-year overall period – 2008 through 2015 – for their analysis. Within these eight years, they build a five-month average to which the post-Sandy Hook period is compared, and ultimately found that the post-Sandy Hook surge in gun sales is linked to 57 additional fatal firearms accidents in the same period.
This overall period includes the year with the lowest number of fatal firearms accidents on record (2015), which continued the long-existing downward trend, but excludes all years before 2008 when fatal accidents were considerably higher. This serves to water down the average, making the number of fatal accidents in the post-Sandy Hook period seem shockingly large.
There were 64 fatal accidents in December 2012, 57 in January 2013, 41 in February, 47 in March, and 37 in April. Levine and McKnight claim that nearly a quarter of these should be attributed to the increase in gun sales after the Sandy Hook school shooting. But there were 50 fatal firearms accidents in November 2012, 59 that July, and 69 in the previous November – suggesting that no such spike really occurred. The chart below shows the total number of fatal firearms accidents per month and indicates that the Post-Sandy Hook Window saw a similar number of tragic but fortunately rare fatal accidents as previous months.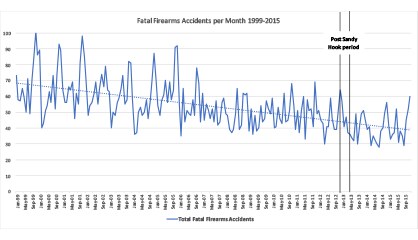
Another issue with the research in Science Magazine is that of the NICS checks used as a proxy for gun sales, with the usual caveat, that this is not a perfect 1:1 proxy. December 2012 was one of the busiest months ever for NICS (second only to December 2015) but the 8th busiest day of all time was in November 2012- before Sandy Hook. Levine and McKnight did not account for the total firearms accumulated prior to December 2012. In other words, they are attributing all of the accidents in the Post-Sandy Hook Window specifically to firearms purchased in that same period while ignoring the more than 150 million guns purchased (using their own proxy) before Sandy Hook. They have no way of isolating fatal injuries that involved only the firearms purchased in the Post-Sandy Hook Window.
Levine and McKnight acknowledge that “simple comparisons of trends over time, for instance, indicate a negative correlation between gun sales and accidental gun deaths. Such comparisons, though, do not account for the presence of other trends that confound these statistics.”
Sandy Hook was sadly neither the first nor last time anti-gun politicians sought to curtail the rights of law-abiding Americans because of the actions of a criminal, leading to an increase in gun sales. The trends that Levine and McKnight insist confound the simple correlation between more guns and fewer fatal accidents are built into the data.
Of course, criminologist Gary Kleck had a much simpler response to Levine and McKnight: “Notwithstanding its prestigious outlet, this paper is junk science, and should never have been published.”















 More Like This From Around The NRA
More Like This From Around The NRA








